Hangar H75 - SAEI
General information
-
Home page
www. buildair.com
-
Location address
Jeddah Airport Base
-
Location country
Saudi arabia
-
Year of construction
2019
-
Name of the client/building owner
Saudi Aerospace Engineering Industries - SAEI (KSA)
- Function of building
-
Degree of enclosure
Fully enclosed structure
-
Climatic zone
Arid - dry and hot all year
-
Type of application of the membrane
covering
Description
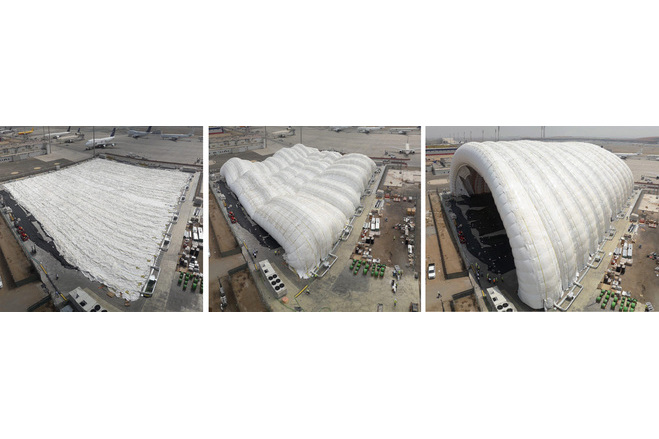
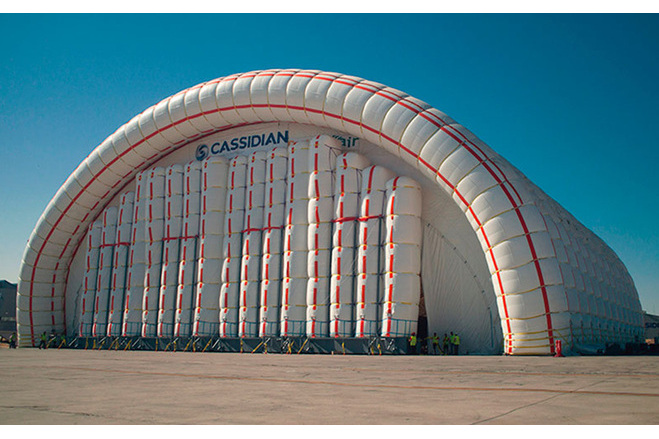
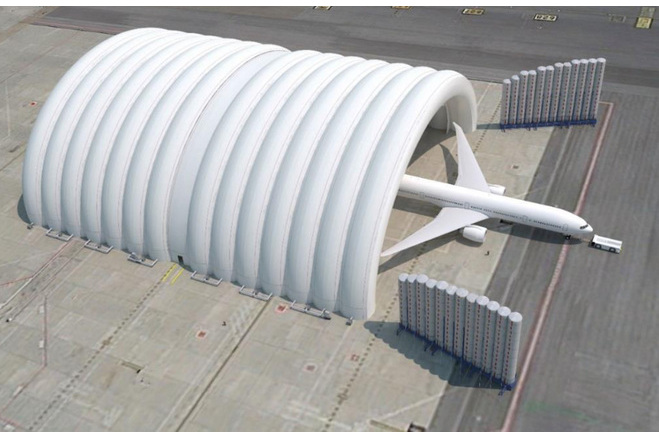
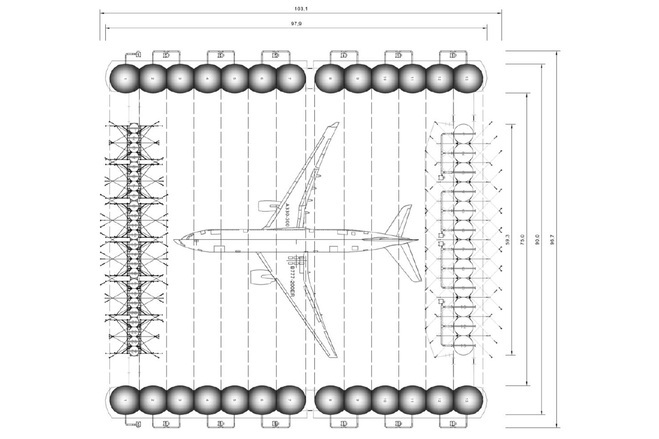
At first glance, the most striking thing about the hangar are its overall dimensions: 97,9m in length, 90m in width (corresponding to 75m of free interior span) and 33m outer height corresponding to 25,5m of free vertical interior height. The main body is based in a succession of 13 inflated tubes that are reinforced by belts and anchored to the base slab. It is complemented by two inflated vertical enclosures at both ends. Note that the tubular arches are pressurized but the utilisation space is not. There is no pressure difference inside/outside and therefore special airtight gates are not necessary.
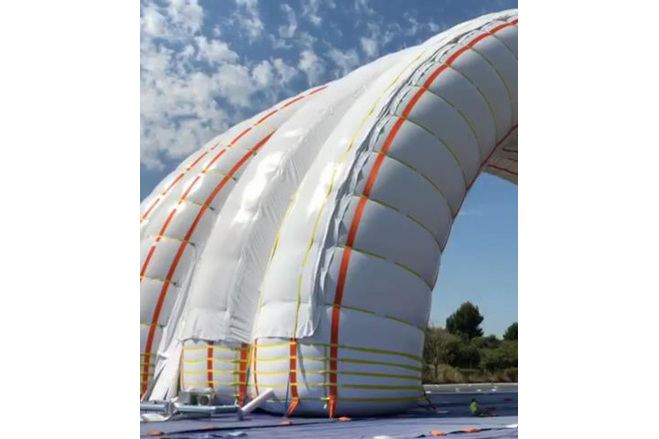
The tubes of the main body are Ø 7,5m in diameter and curved, forming a 90x33m semi-elliptical outer profile. They are inflated at a low pressure of 20mbar, that could be increased to 25mbar in case of peak wind loads. The internal pressure provides shear and bending rigidity to hold the loads acting over the structure and minimize deformations.
The inflated tubes are bounded by a net of belts as a cage to limit the deformations and to transmit the internal forces to the anchoring points. Three different types of belts have been designed depending on the structural behavior and internal forces expected:
1) spines and ribs following the direction of the tubes. They bear the bending forces and reduce the deformation in this direction.
2) braces around the tubes keep their cohesion and bear the circumferential component of the stress and deformations in the membrane mainly produced by the internal pressure.
3) radial belts and crosses placed between tubes increase the stiffness in this plane, which is very relevant for the wind lateral load.
All the belts are connected to each other to configure a tensioned network in such a way that forces are transmitted axially to the anchorage points avoiding bending and compression.
The main body includes an additional membrane surrounding the whole set of tubes conceived as a protector layer against the sun radiation and waterproof to ensure the requirements related to water leaks or air entrance through the interphase between the tubes.
The front enclosure is the entry and exit door of the aircraft. It relies on air-inflated to 30mb internal pressure to bear the external actions. They are surrounded by belts, hold by vertical beams and placed on steel carriages that move. Every carriage is 10m wide and the top surface is raised 1m above the ground. The tubes have a diameter of 2,257m while their height is variable from 12,5m to 20,5m because the geometry of the enclosure follows the semi-elliptic shape of the hangar. A set of supporting cables is built at both sides of the enclosure in order to increase its stability. The back enclosure is non-movable and relies also on air-inflated vertical tubes, 5,1m in diameter and a variable height from 14,87m to 19,75m according to the shape of the enclosure. They are inflated to 30mbar of internal pressure and, together with their surrounding belts, they are supported by vertical beams anchored directly to the ground.
Description of the environmental conditions
Material of the cover
-
Cable-net/Fabric/Hybrid/Foil
Fabric
-
Material coating
PVC coated polyester fabric with surface treatment SIOEN TT0117E
Main dimensions and form
-
Covered surface (m2)
8811
-
Maximum height (m)
25.5
-
Total length (m)
97.9
-
Total width (m)
90
Duration of use
-
Temporary or permanent structure
Permanent
-
Convertible or mobile
Convertible and mobile
Involved companies
-
Contractors
BuildAir Engineering & Architecture
-
Suppliers
SIOEN Industries
Editor
-
Editor
Evi Corne